Why do you need a Data Protection strategy? Keep your information safe at all times through a multi-layered plan and prepare in case the unthinkable happens.
Data protection is the process of protecting digital information throughout its entire life cycle and safeguarding the data from unapproved access. Securing data in an organization is the most important jobs, secure data helps improve efficiency and productivity while reducing risks and finding solutions. In simpler terms, Data protection is the practice used to manage confidential data.
Data protection utilizes the latest technologies and processes while being compliant with privacy laws and policies to protect digital information throughout its life, from creation to when it is eventually disposed of.
The core concept of a sound Data protection strategy is to mitigate both internal and external threats. Be it data breaches, personalized attacks, or accidental mishandling and possible malfeasance.
Why do companies require a Data Protection Strategy?

In just the third quarter of 2024, over 422 million personal records were compromised. This was a global phenomenon. Companies have paid out 4.89 million US dollars as the average cost of a data breach. Businesses today face numerous challenges while trying to keep sensitive data confidential; it is safe to say that a robust Data Protection strategy is crucial for any organization.
The main risks a comprehensive security strategy helps to protect against are as follows:
- Data loss due to cyberattacks: These usually come in the form of ransomware and malware attacks. The purpose of these attackers is to gain control over sensitive data that is otherwise inaccessible. Recovering data in case of these attacks can take up to weeks, if not months.
- Compliance penalties: Businesses must always operate under regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, GDPR, NIS2, and more. Even accidental mishandling of information can result in a huge fine for the companies.
- A mark on reputation: The company is reputable as long as the customer’s data is safe. In case of a single data breach, all of the faith and trust in the organization goes away, tarnishing credibility forever.
- Security challenges: More organizations are opting for hybrid and multi-cloud environments. The curated services these models offer are beneficial to everyone, but they increase the attack surface and create new vulnerabilities at the same time.
- Insider threats: Most employees are ignorant of data protection strategies, and thus, take little to no time trying to keep information confidential. Accidents happen all the time. Whether the information was leaked because of negligence or malicious intentions, the fact remains that it places the company at risk.
Data Protection Strategy: Key Components
A protection strategy is less about ticking boxes and more about being constantly vigilant and assessing potential threats that could put your organization at risk of a data breach.
A key component helps businesses integrate data protection seamlessly into their operations without it feeling like a massive challenge. Some of them to keep in mind are as follows:
Data lifecycle management
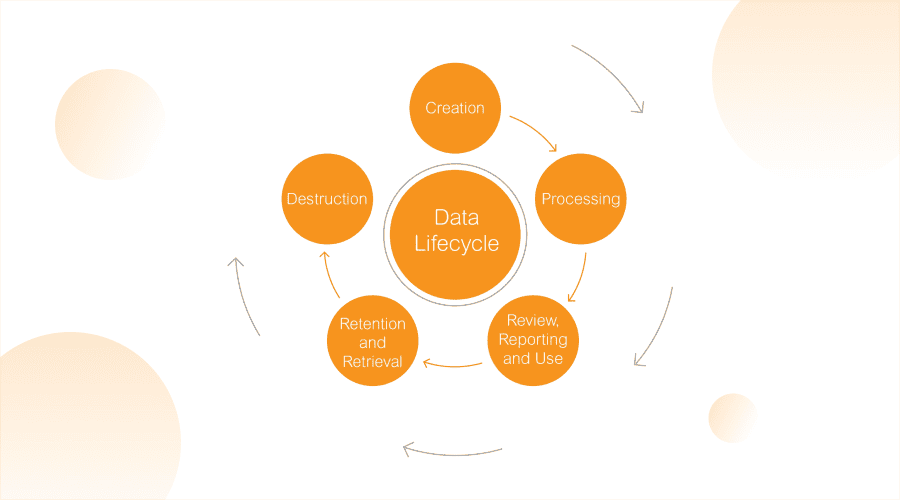
Just like everything else, Data also has a beginning, middle, and end. A lifecycle management plan takes into account all stages of its life, from creation to disposal, while ensuring the information is secure and accessible. The strategy also considers privacy requirements that need to be met. A sound strategy implements clear workflows and tries to automate the process, which reduces risks, clutter, and streamlines processes.
Data Accessibility
An organization’s data should not be accessible to everyone. To keep data confidential, it is essential to implement principles that are based on zero trust. Practices like role-based access controls (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) help protect sensitive information from unauthorized personnel. Regular audits done by approved users can help seek out possible vulnerabilities, which reduces the risk of data breaches significantly.
Data Encryption
Imagine your belongings locked in a vault and only you have the key. This is the idea behind encrypting data. This is done by converting information from human languages to unreadable code. This should be done at all times, whether the data is in transit or is stored. Along with secure key management, Capable encryption algorithms ensure attackers can gain nothing even if they manage to successfully penetrate the system. Lines of ciphertext aren’t helpful to anyone.
Risk Management
Risk Management is the process of staying ahead of attackers. You have to figure out the vulnerabilities of your system before cyber criminals. The most common points are found to be outdated systems with security updates halted for months, and ignorant employees. Getting on top of these things, along with patch management and access reviews, can help keep potential threats at bay.
Backup and Recovery
Creating an additional copy of your data does not count as a backup. Backups are the lifeline of an organization during attacks and data breaches. An effective data backup and recovery strategy encompasses immutability, keeping the information from being doctored and ransomware resistant. Companies are encouraged to test their disaster recovery plans frequently, ensuring efficiency when it matters.
Storage Management
It is imperative that companies follow proper guidelines when collecting and storing data. Data storage management is the practice of securing data during transfers and during the time it is stored. Storing data raises another question: whether keep it on-site, in a cloud environment, or adopt a hybrid setup. A hybrid storage setup balances security and accessibility while protecting information from leaks and data breaches.
Incident Response
Stopping every cyber attack isn’t possible. With emerging technology and AI-powered capabilities, attackers are exploiting new vulnerabilities each day. The only thing organizations can fully control is their response. An effective response strategy would allow the company to minimize damage, isolate compromised sections, and aim to resume normal daily operations as quickly as possible. Testing this plan routinely helps boost confidence in employees and keeps you equipped for disasters.
Monitoring the landscape
Cyber threats are evolving every day, and so should organizations’ defenses. Companies must make use of automated real-time monitoring tools that can help mitigate potential threats before they are allowed to escalate. It is also important to be updated with privacy regulations, which are evolving at the same time.
Best Practices for Data Protection
Devising an effective Data Protection strategy is a challenging task. Here are some widely accepted practices to help organizations achieve a comprehensive plan for data security.
- Know your data: Authorized individuals must always be aware of where sensitive data is being stored. Regular audits must be conducted, which helps identify vulnerabilities and approved users. This can also reduce clutter by flagging redundant entries and outdated files.
- Classification is the key to fortitude: All the data in an organization is not of equal importance. It is necessary to categorize information and determine access levels. It helps prioritize resources where they are needed the most. Staying compliant with privacy regulations is also much easier when a precise classification system is implemented.
- Multiple layers of Defense: Organizations should build their defense in layers, utilizing various technologies and strategies. Using firewalls, data encryption, safe web browsing, and more. Implementing a multi layered defense eliminates weak spots spread around the system and ensures a single vulnerability isn’t the point of failure.
- Immutable Backups: The number of backups does not matter if they are not immutable, that is, tamper-proof. Ensuring the organization has reliable backups is paramount. Testing and updating them is also recommended to avoid uncertainty during cyber attacks.
- Reduce Ignorance: The leading cause of data breaches, sadly, still remains to be human error. The inability to detect phishing sites and malicious links, paired with weak passwords, is a recipe for disaster. Everyone in the team should be well-versed in identifying suspicious links and websites. Adopting these habits along with strong password generation and management keeps mistakes to a minimum.
- Zero Trust Architecture: This is the best practice any organization can implement. Zero trust strategy does not assume the threat is on the outside, but rather sees all users as potential threats. Traditional security models seldom focused on the network and assumed everything within it was safe. A Zero trust security model is based on the opposite of this notion. All users and every device must go through multiple authorization checks to gain as well as maintain access to data within the environment. Companies stand a chance to significantly enhance their data security capabilities a lot through the implementation of practices such as this.
Prepare for the worst
As the saying goes, “Hope for the best, but plan for the worst.” An effective Data protection plan utilizes every weapon in the organization’s arsenal and hopes to keep attackers at bay and the damage to a minimum. But this isn’t always the case. In case of a data breach, employees must be aware of what they should be doing. A robust data protection strategy plans for every scenario, especially the worst one.