The Domain Name System (DNS) is a vital component of today’s interconnected web. It connects users to websites and services. DNS hijacking is also understood as DNS redirection. This is when an attacker gains control of a DNS server to redirect traffic from legitimate websites to malicious or fake ones.
This can lead to financial loss and theft of sensitive information. It is necessary to know how to identify DNS hijacking and what to do to stop it from happening. This paper will clarify what is DNS hijacking. How to detect and fix it.
What is DNS hijacking?
DNS hijacking refers to a cyber attack in which an attacker gains control of a DNS server and redirects traffic from legitimate websites to malicious or fake websites. DNS systems translate domain names into IP addresses. This allows users to access websites with simple domain names instead of difficult numerical IP addresses.
An attacker can hijack the DNS server to divert users to fake sites that look real. This allows them to swipe important data like login credentials, monetary data, and private information. There are many ways to hijack DNS servers, including malware, social engineering, and phishing. It is essential to detect and fix DNS hijacking in order to protect your online activities as well as data.
What types of DNS hijacking?
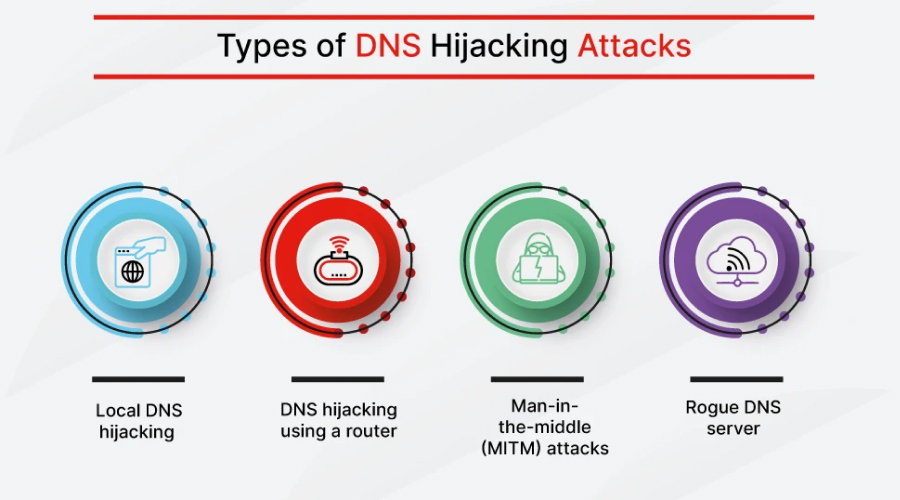
DNS hijacking is a very common cyber attack. It can happen in many different ways. Pharming is one type of DNS hijacking. This involves attackers compromising a DNS server to redirect traffic to a fake site, usually a phishing website. DNS spoofing is another type of DNS hijacking. This involves attackers inserting false information into DNS caches to redirect traffic to malicious sites.
Credit: Fortinet
Man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM) are another form of DNS hijacking. These attacks intercept traffic between the DNS server and the user to redirect it. DNS tunneling, which is an attack that uses DNS queries to bypass security checks and connect with a malicious server, is another type of DNS hijacking. These attacks are very serious, and you must be alert to them so that you can prevent them.
How do you detect DNS hijacking?
It can be difficult to detect DNS hijacking because it can happen without the user being aware. There are some indicators that may be indicative of a DNS hijacking attack. Unexpected website redirects are a common sign. This is when the user is redirected from a website they didn’t intend to visit.
Changing your DNS server settings, such as a new default DNS Server or DNS entries you did not add, is another sign. DNS hijacking can also lead to DNS lookup errors and the inability access certain websites. Regularly check your DNS settings on your device and look out for unusual activity. Antivirus and anti-malware software are also useful in detecting and preventing DNS hijacking.
How to stop DNS hijacking
It is crucial to prevent DNS hijacking in order to protect your online activities as well as data.
These are the leading practices to prevent DNS hijacking.
- Reputable DNS servers are essential: DNS hijacking can be prevented by using a trusted DNS server. Use the DNS server that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or public DNS servers such as Google Public DNS and Cloudflare DNS.
- DNSSEC is an extension of DNS System Security Extensions: DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions), a protocol that increases security in the DNS system, digitally signs DNS records to verify their authenticity. DNSSEC can be disabled on your device. You can also use DNS servers that support it to prevent DNS hijacking.
- Maintaining your software current is key to preventing DNS hijacking. Security patches are often included in software updates that fix exposures that attackers can manipulate.
- Two-factor authentication is recommended: Two-factor authentication makes it more difficult for hackers to gain entry to your online accounts, even if they hijack your DNS to obtain your login credentials.
- Use VPN: Virtual private networks (VPNs) encrypt your internet traffic and route it via a secure server to prevent DNS hijacking or other attacks.
- Be wary of suspicious emails and website addresses: Phishing emails or visits to fake websites can all be used to hijack DNS. Avoid clicking on links or extensions from anonymous sources, and be careful with emails.
These methods can be used to control DNS hijacking and safeguard your online actions.
Examples of DNS hijacking
DNS hijacking is a popular cyber attack that attackers have used in various instances.
These are only some instances of DNS hijacking attacks.
- Sea Turtle: A hacking group called Sea Turtle stole the DNS records for several high-profile organizations, including telecom companies and internet infrastructure providers, in 2019. This was used by the attackers to redirect traffic to fake sites to steal login credentials.
- DNSpionage: DNSpionage was a cyber-espionage campaign in 2018 that used DNS hijacking as a means to gain access to Middle East government agencies and businesses. To steal information, the attackers compromised DNS servers at targeted organizations and redirected traffic to fake websites.
- The New York Times: In 2013, The New York Times reported on a hacker who used DNS hijacking in order to redirect users to a fake site designed to steal login credentials.
These examples illustrate the potential consequences of DNS hijacking and the importance to prevent and detect it.
FAQs
1. Can DNS hijacking affect my mobile devices?
DNS hijacking is possible on all devices connected to the internet.
2. Does a VPN help me avoid DNS hijacking?
A VPN can help protect you against DNS hijacking. It encrypts your internet traffic, routes it through secure servers, and prevents attackers from intercepting DNS requests.
3. What can I do to prevent DNS hijacking?
DNS hijacking can be prevented by changing your DNS server settings. It is important to make sure that the DNS server you choose does not allow for attacks.
4. How can attackers gain access DNS servers?
Hackers can gain access DNS servers by a variety of means. These include exploiting vulnerabilities in DNS software, brute-force attacks that guess login credentials, or social engineering attacks that trick users into divulging their login credentials.
It is possible to recover from a DNS-hijacking attack. To do this, reset your DNS server settings and remove any malware or malicious software. You can also change your login credentials for affected accounts. It is important to keep an eye on your accounts and report any suspected breaches to the appropriate authorities.
In conclusion, DNS hijacking is a cyber-attack that can seriously affect individuals or organizations. This involves hackers intercepting DNS requests and redirecting them to fake websites. They can steal sensitive information or infect computers with malware. It can be challenging to notice DNS hijacking. However, signs such as unexpected website redirects and changes in DNS server settings could indicate that an attack is underway.
DNS hijacking can be prevented by using reliable DNS servers. Enable DNSSEC, keep your software up-to-date, use two factor authentication, and be cautious of dubious emails.
It is essential to take steps to restore your DNS settings in the event of a DNS hijacking attack. This includes changing your login credentials, removing malware, and resetting DNS server settings. Individuals and companies can take these steps to protect themselves against the potential dangers of DNS hijacking. This blog will explain what DNS hijacking is. We hope this article on ”what is DNS hijacking? How to detect and fix it” is useful to the readers.






