
Power BI 2026 enhances team collaboration with advanced new features. From workspace management to sensitivity labels, learn what’s new with the 2026 Power BI update.
Collaboration in analytics has moved on to become a necessity for modern data-driven organisations and Microsoft has been watching this shift for a long time to bring powerful collaboration features to Power BI. Teams across every department need to create, share, and manage insights more efficiently. Power BI 2026 and Microsoft Fabric are now packing in powerful collaboration tools to support teamwork across complex projects. These new features are designed to help teams work smarter. From advanced workspace management to impact analysis and beyond, here is everything you need to know.
Latest collaboration features in Power BI
Collaborative workspaces
Workspaces are the foundation of collaboration in Power BI 2026. Workspaces act like shared environments where multiple users can co-create and edit multiple things like reports, data model and more while maintaining clear organisation and access control. Proper workspace management will ensure teams have access to the right tools without duplication.
➢ Types of workspaces
Power BI offers two different types of workspaces. These are
1. App workspaces
Collaborative spaces designed for team projects. This type of workspace hosts multiple users who can create, edit, and publish dashboards and reports. App workspaces also host your semantic models and dataflows to allow teams to build complex analytics solutions together.
2. Personal Workspaces (My Workspace)
Every user has a private workspace for experimentation and personal projects. Admins have the option of converting these into a collaborative workspace later to retain valuable insights created by individual team members.
These different types of workspaces allow for better structured collaboration. Teams can prototype reports in personal workspaces and then migrate them to app workspaces for wider use.
➢ Managing workspace states
Workspaces in Power BI have defined states. This is so the admins can monitor and maintain smooth collaboration.
- Active: Ready for team use
- Orphaned: Missing an admin and requires administrative intervention
- Deleted: In a retention period. Recovery is possible
- Removing: Final stage before permanent deletion
- Not Found: Workspace not recognised in the tenant
Administrators can prevent disruption in collaboration by tracking these states. Say for example a critical app workspace becomes orphaned. What can admins do? They can quickly assign a new admin to maintain team access.
Governance features for seamless team collaboration
Power BI 2026 brings administrators all the tools they need to manage access, control workspace capacities, and enforce organisational policies while letting teams work flexibly.
➢ Workspace options in the admin portal
The Admin portal offers a ribbon and More Options menu to manage workspace functionality. These are amazing tools to help teams work efficiently.
- Refresh: Keeps the workspace list up to date
- Export: Share workspace details for reporting or audits
- Edit: Update workspace names and descriptions for clarity
- Access management: Add or remove members
- Recover and restore: Quickly restore deleted or orphaned workspaces to prevent work loss
- Capacity assignment: Assign workspaces to Premium capacities to guarantee performance for larger datasets.
➢ My Workspace governance
Admins also have control over personal workspaces to enable collaborative support:
- Get temporary access to any My Workspace to assist or audit.
- Assign default capacities for personal workspaces.
- Block users from reassigning My Workspaces to unauthorised capacities.
- Convert deleted personal workspaces into collaborative app workspaces to retain valuable reports.
Admins use these features to balance user autonomy and organisational governance to allow teams to innovate.
➢ Tenant settings to support team collaboration
Tenant-level settings bring on more control over how teams interact with Power BI:
- Create workspaces: Limit workspace creation to certain users or groups to prevent uncoordinated projects.
- Publish apps: Control who can distribute dashboards and reports across the organisation so that only vetted content reaches users.
- Use semantic models across workspaces: Teams can now reuse models to reduce redundancy and extra work.
- Block reassigning personal workspaces: Prevent changes that might compromise compliance when moving workspaces across capacities or regions.
Organisations are now able to scale collaboration safely to provide structure without stifling creativity.
Data lineage
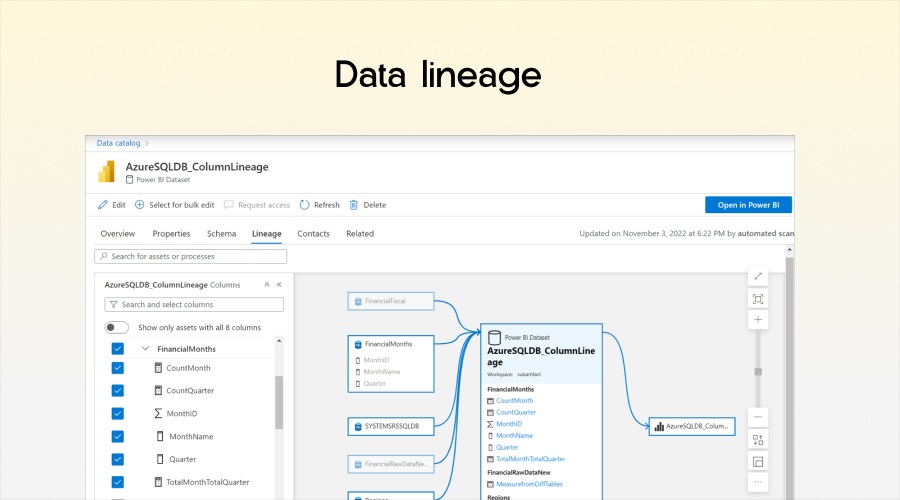
With projects becoming more complex than ever before, teams must understand how data moves through their analytics ecosystem. Power BI introduces lineage view to help teams visualise and trace dependencies between data sources, models, and reports.
➢ Exploring Lineage View
Lineage view shows relationships between:
- Dashboards and reports
- Semantic models and dataflows
- External data sources
Teams can track upstream and downstream dependencies to identify how changes in one artefact affect others. This visibility reduces errors and ensures consistent insights.
➢ Interactive features
Lineage view comes with interactive tools to improve navigation:
- Zoom and pan across the lineage canvas for detailed exploration
- Highlight a specific artefact to focus on related items
- View metadata such as last refresh times, certification status, and source workspace names.
For example, if a marketing team updates a dataflow connected to multiple dashboards, the lineage view shows all affected dashboards. So it becomes super easy for teams to coordinate updates and prevent broken reports.
Impact analysis
Power BI now allows teams to make changes confidently through impact analysis. This feature shows the potential effect of modifications to semantic models or data sources.
➢ Semantic model impact analysis
Semantic model impact analysis shows:
- Which workspaces, reports, and dashboards might be affected
- Usage metrics including unique viewers and total views, to prioritise changes
- Notifications to relevant team members to keep them informed.
This will ensure teams coordinate updates effectively. For example, updating a heavily used sales dashboard can be planned without inadvertently affecting other departments relying on the same semantic model.
➢ Data source impact analysis
Data source impact analysis helps teams manage dependencies across the organisation:
- Identify all workspaces, dataflows, and models using a data source.
- Detects duplication to support consolidation and a single source of truth.
- Notifies affected teams when the data source changes.
Together, semantic model and data source impact analysis enhance collaboration by providing teams with the much-needed transparency and predictability so teams can now work without breaking each other’s reports.
Sensitivity labels
Collaboration will inevitably involve sensitive data. Power BI integrates with Microsoft Purview Information Protection to allow teams to apply sensitivity labels that protect content.
➢ Applying labels in Power BI
Apply labels in dashboards, reports, semantic models, and dataflows using the Settings menu. Labels enforce permissions automatically so only authorised users can access sensitive information.
➢ Applying labels in Power BI Desktop
- Set sensitivity labels on PBIX files directly from the toolbar.
- Publishing or uploading labelled files to the service applies the labels to all associated reports and models.
- If the PBIX file replaces existing assets, users can choose to retain or overwrite existing labels.
- Managing labels across teams
- Notify team members when sensitivity labels change to keep everyone on the same page.
Admins can enforce labels across collaborative projects for better compliance with organisational and regulatory standards.
For example, a finance team can label quarterly earnings reports as “Highly Confidential.” This prevents accidental exposure while still allowing collaboration among authorised team members.
Best practices for team collaboration in Power BI 2026
- Use workspaces strategically: Centralise projects for team access and prevent scattered reports.
- Use lineage view: Ensures changes in one dataset or model do not disrupt other projects.
- Apple sensitivity labels consistently: Protect sensitive content while allowing controlled collaboration.
- Monitor workspace capacities: Assign Premium capacities to high demand workspaces to maintain optimal performance.
- Restrict workspace creation: Prevent uncoordinated projects while still encouraging team innovation.
- Coordinate impact analysis: Regularly perform semantic model and data source impact checks before updates.
Conclusion
Power BI 2026 brings powerful collaboration features for modern teams bringing in multiple features like workspace management, lineage tracking and a whole lot more. Teams can now work together with confidence and organisations that leverage these features empower teams to create, share, and manage analytics efficiently, enabling faster decision making and consistent insight across the enterprise.
Power BI makes collaboration productive, secure, and scalable so that teams have all the tools to succeed in a data-driven world.
Also Read: Microsoft’s Copilot Pro Brings AI-Powered Office Features in Subscription-Based AI Plan






