Software Quality Assurance (QA) is a crucial part of successful software development. It is a systematic process that makes sure your final product is of the highest quality, reliable, and satisfies users. You can think of QA as your safety net, it catches potential issues before they reach your end users, protecting both your reputation and your bottom line.
In today’s competitive software industry, it is extremely important to have strong QA best practices in place. By incorporating quality assurance into every stage of your development process, you are not just testing code; you are also instilling confidence in your product’s ability to perform in real-world situations. QA covers everything from validating initial requirements to monitoring after deployment, providing a complete defense against defects and performance problems.
Modern software development requires a strategic approach to quality that goes beyond traditional testing methods. You need practices that can adapt to agile methodologies, embrace automation when appropriate, and still include the human insight that only manual testing can provide.
Understanding Software Quality Assurance in SDLC
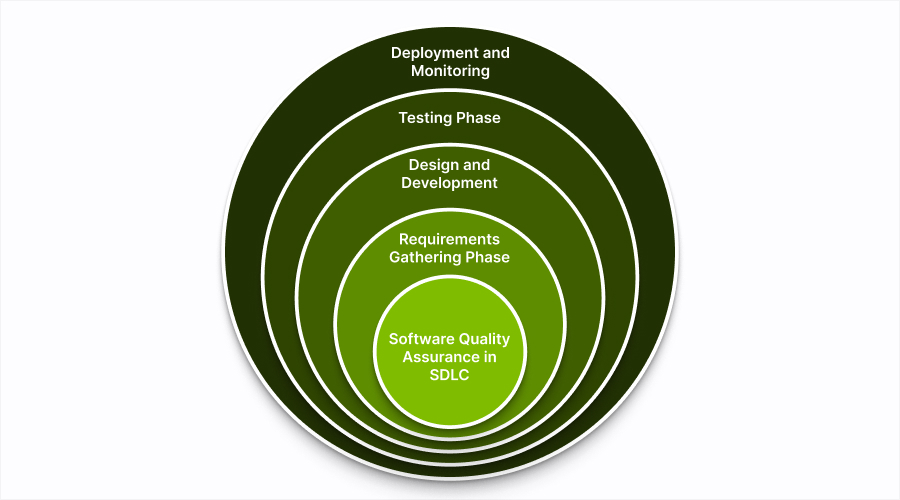
The quality assurance process is an integral part of every phase of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It creates a comprehensive framework that ensures software excellence from start to finish. This systematic approach makes quality an essential part of development instead of something that is considered only after the fact.
1. Requirements Gathering Phase
During this phase, QA professionals work closely with stakeholders to define requirements that can be tested and establish quality criteria. You’ll find that clear and measurable requirements are crucial for developing effective testing strategies.
2. Design and Development
The software testing lifecycle begins while developers are writing code. QA teams start planning tests and creating test cases based on design documents. They also create test scenarios that align with architectural decisions.
3. Testing Phase
Different types of testing are carried out simultaneously during this phase. Unit tests validate individual components, while integration tests verify how different parts of the system interact with each other. Both manual exploration and automated regression suites can be used during this critical stage.
4. Deployment and Monitoring
After the software is deployed, it is important to monitor its performance and gather feedback from users to ensure stability in production. This ongoing monitoring helps identify any issues before they affect users, and following established standards ensures consistency across different releases.
This integrated approach significantly reduces the cost of fixing defects – catching issues during the requirements phase is 100 times less expensive than fixing them after they have gone into production.
Diverse Testing Types for Comprehensive Coverage
Effective QA requires implementing multiple testing approaches, each serving distinct purposes in validating software quality.
➢ Understanding Different Testing Approaches
- Black-box testing: Examines functionality without knowledge of internal code structure, focusing on input-output relationships and user experience.
- White-box testing: Analyzes internal code paths, logic branches, and structural components to ensure thorough coverage.
➢ Validating Code Quality
- Unit testing: Validates individual code components in isolation, catching defects at the smallest functional level.
- Integration testing: Verifies that separate modules work correctly when combined, identifying interface issues and data flow problems.
- Regression testing: Ensures that new changes don’t break existing functionality, maintaining system stability throughout development cycles.
➢ Ensuring Application Stability
- Smoke testing: Performs basic sanity checks on critical features, confirming that the application is stable enough for deeper testing.
- User acceptance testing: Involves end-users validating that the software meets business requirements and real-world usage scenarios.
You should implement these testing types strategically based on your project’s risk profile, timeline, and resource availability. Each type addresses specific quality aspects that others might miss, creating a comprehensive safety net for your software releases.
Balancing Manual and Automated Testing Approaches

Finding the right balance between manual testing and automation creates a strong quality assurance strategy that maximizes efficiency while maintaining thorough coverage. Automated testing tools like Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG excel at handling repetitive tasks with precision and speed.
➢ When to Use Automation
Automation delivers significant advantages for specific testing scenarios:
- Unit tests run consistently across code changes, catching regressions immediately
- Regression testing executes hundreds of test cases in minutes rather than hours
- Data-driven tests process multiple input combinations without human fatigue
- Cross-browser compatibility checks run simultaneously across different platforms
➢ The Role of Manual Testing
Manual exploratory tests remain irreplaceable for scenarios requiring human judgment and creativity. You need human testers to evaluate user experience flows, identify usability issues, and explore edge cases that automated scripts might miss. Complex business logic often requires contextual understanding that only experienced testers can provide.
➢ Finding the Right Balance
The most effective QA teams allocate approximately 70% of repetitive testing to automation while reserving 30% for manual exploration. This approach ensures How to Ensure Quality in Software Development: QA Best Practices by combining the speed of automation with the insight of human intelligence.
Early and Frequent Testing through Shift-Left Strategy
Shift-left testing changes the game for traditional QA methods by moving testing activities earlier in the software development process. Instead of waiting until development is complete, you integrate testing during requirements gathering, design phases, and initial coding stages.
This proactive strategy transforms how you identify and address potential issues:
- Requirements validation catches ambiguities before coding begins
- Design reviews expose architectural flaws early in the process
- Unit testing during development prevents defects from spreading
- Code reviews identify quality issues at the source
The financial impact is significant. Fixing defects found during the requirements phase costs about 10 times less than fixing those discovered during system testing. Post-deployment fixes can cost up to 100 times more than early-stage corrections.
You also gain additional benefits such as reduced debugging time, improved code quality, and faster delivery cycles. Development teams spend less time troubleshooting complex integration issues when problems are identified early on. This approach also encourages better collaboration between developers and testers, creating a shared responsibility for quality throughout the development process instead of treating testing as a final checkpoint.
Risk-Based Testing to Prioritize Critical Areas
Risk-based testing transforms your QA approach by strategically allocating testing resources based on potential impact and likelihood of failure. This methodology ensures you focus your limited testing time and budget on the features that matter most to your users and business objectives.
➢ How to Assess Risks in QA
Risk assessment in QA begins with identifying components that pose the highest threat to system stability, user experience, or business operations. You evaluate each feature considering factors like:
- Business criticality – Revenue-generating functions, user authentication systems
- Technical complexity – New integrations, third-party dependencies, legacy code modifications
- Usage frequency – Core user workflows, high-traffic features
- Failure impact – Data loss potential, security vulnerabilities, performance bottlenecks
This strategic approach prevents the common pitfall of spending excessive time testing low-risk areas while critical functionalities receive insufficient attention. You create a testing priority matrix that guides your team’s efforts toward maximum value delivery.
➢ When to Use Risk-Based Testing
Risk-based testing becomes particularly valuable when working with tight deadlines or resource constraints, ensuring quality where it counts most.
Integrating CI/CD with QA
CI/CD pipelines change quality assurance from a delay into a faster way to deliver software. Tools like Jenkins and Travis CI automate the entire build and test process, running quality checks every time developers commit code changes to the repository.
These platforms manage complex workflows that include:
- Automated unit test execution immediately after code compilation
- Integration testing across multiple service dependencies
- Regression test suites running against the latest build
- Code quality analysis using tools like SonarQube or ESLint
- Security vulnerability scanning before deployment
You get immediate feedback when CI/CD tools find failing tests or quality gate violations. This quick response system stops faulty code from moving forward in your deployment pipeline. Jenkins is great for large businesses with its wide range of plugins, while Travis CI works well with open-source projects on GitHub.
The automation removes the need for manual work in repetitive testing tasks, letting your QA team focus on exploratory testing and complex scenario validation. Each successful pipeline run increases confidence in your software’s readiness for production deployment.
Developing Comprehensive Test Plans and Documentation
Test planning is crucial for successful quality assurance initiatives. You need detailed test plans that align with your chosen development methodologies, whether you’re working within Agile sprints, Waterfall phases, or DevOps cycles.
Effective test plans should include:
- Clear test objectives tied to specific requirements and user stories
- Detailed test cases with precise steps, expected results and success criteria
- Resource allocation specifying team members, tools and timeframes
- Risk assessment identifying potential bottlenecks and mitigation strategies
- Entry and exit criteria defining when testing phases begin and end
Your documentation must be living assets that evolve with your project. Test cases require regular updates to reflect changing requirements, while test execution reports provide valuable insights for future planning cycles.
Tools like TestRail, Zephyr or qTest can streamline your test planning process by providing centralized repositories for test cases, execution tracking and reporting capabilities. These platforms integrate with popular project management tools, ensuring your QA documentation stays synchronized with development progress and maintains traceability throughout the entire software development lifecycle.
Fostering Effective Collaboration Among Teams
Team collaboration in QA is essential for successful software delivery. Testers, developers and product owners need to work together seamlessly to find defects early and maintain quality standards throughout development.
➢ Establishing Daily Stand-Ups
Setting up daily stand-ups creates regular opportunities for team members to share updates, discuss obstacles and exchange testing insights. When developers understand what testing tasks are most important and testers are aware of any limitations in development, it reduces communication gaps that can lead to missed requirements or delays in releases.
➢ Creating Shared Communication Channels
Using tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for shared communication channels allows for immediate problem-solving. Critical bugs can be quickly escalated, requirements can be clarified and test scenarios can be discussed without having to wait for formal meetings. This quick feedback loop speeds up issue resolution and keeps projects moving forward.
➢ Implementing Cross-Functional Pairing Sessions
Organizing cross-functional pairing sessions between testers and developers helps both parties understand each other’s perspectives on code quality and testing methods. When a tester works alongside a developer during exploratory testing, they both gain valuable insights that enhance the overall quality of the product.
➢ Conducting Regular Retrospectives
Holding regular retrospectives gives teams the opportunity to identify any obstacles in collaboration and make improvements. Workflow inefficiencies, communication breakdowns, or limitations in tools can be addressed during these sessions, fostering a culture of continuous improvement in your QA processes.
Utilizing Metrics to Measure QA Effectiveness
QA metrics are essential for improving software quality and making informed decisions. They provide specific measurements to assess the effectiveness of your testing efforts and pinpoint areas that need improvement.
➢ Key Metrics for QA Evaluation
Here are some crucial metrics you should consider:
- Test Coverage: This metric indicates the percentage of code that has been tested. It gives you insight into which parts of your application have not undergone testing. You can measure test coverage using different methods such as line coverage, branch coverage or function coverage based on your testing objectives.
- Defect Density: Defect density measures the number of defects in relation to the size of your codebase. It is usually expressed as defects per thousand lines of code (KLOC). This metric helps identify modules with significant issues and allows for comparison of quality across various components.
- Defect Injection Rate: This key performance indicator tracks the number of bugs introduced during each development phase. By understanding when defects are being injected, you can take proactive measures to prevent them in the future.
- Bug Fix Time: Bug fix time represents the average duration it takes to resolve defects. Monitoring this metric helps you gauge the efficiency of your development team in addressing issues.
- Test Execution Rate: The test execution rate indicates the percentage of planned tests that have been completed. It provides visibility into how effectively your testing activities are progressing.
- Defect Escape Rate: This metric compares the number of bugs found in production with those discovered during testing. A high defect escape rate may indicate gaps in your testing process that need attention.
➢ Tools for Metric Collection and Visualization
To streamline the collection and visualization of these metrics, you can leverage tools like Jira or TestRail. These tools can automatically gather data and present it in a visual format, making it easier for your team to identify trends and make necessary adjustments to testing strategies.
By utilizing these metrics and tools effectively, you can enhance the effectiveness of your QA processes and drive continuous improvement in software quality.
Managing Test Environments for Accurate Results
Effective test environment management is crucial for reliable quality assurance processes. You need dedicated environments that closely resemble production settings while being separate from development activities. This separation prevents code changes from affecting ongoing tests and ensures consistent results throughout different testing phases.
➢ Types of Environments in Your Testing Strategy
Your testing strategy should include multiple environment types, such as those outlined in this comprehensive guide on understanding the types of test environments:
- Development environment – Where developers write and initially test code
- QA/Testing environment – Isolated space for comprehensive testing activities
- Staging environment – Production-like setup for final validation
- Production environment – Live system serving end users
Each environment requires specific configurations, data sets, and access controls. You must maintain version control across these environments to track changes and reproduce issues effectively. Database synchronization becomes critical when testing data-dependent features, requiring regular refreshes from sanitized production data.
➢ The Impact of Environment Stability on Testing Accuracy
Environment stability directly impacts your testing accuracy. Unstable environments lead to false positives, wasted testing cycles, and delayed releases. To counteract these issues, you should implement monitoring tools to track environment health and automate deployment processes to ensure consistency across all testing phases. Following some best practices on how to ensure a stable test environment can significantly improve your testing outcomes.
Incorporating Security and Performance Testing Practices

Modern software applications face unprecedented security threats and performance demands. Security testing serves as your first line of defense against vulnerabilities that could compromise user data or system integrity. This testing approach encompasses multiple layers, from authentication mechanisms to data encryption protocols.
Penetration testing takes security validation a step further by simulating real-world attack scenarios. You can employ both automated tools and manual techniques to identify potential entry points that malicious actors might exploit. Th
Performance testing ensures your application maintains optimal functionality under various load conditions. Performance/load testing tools like LoadRunner and Apache JMeter provide comprehensive solutions for stress testing your systems. These tools simulate thousands of concurrent users, helping you identify bottlenecks and capacity limitations before deployment.
LoadRunner excels in enterprise environments where complex protocols and detailed performance analytics are essential. Apache JMeter offers an open-source alternative with robust scripting capabilities and extensive protocol support. Both tools generate detailed reports showing response times, throughput rates and resource utilization patterns.
➢ Ensuring Accessibility Compliance and API Reliability
Accessibility testing ensures your software remains usable for individuals with disabilities. Following WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards, you can verify that your application supports screen readers, keyboard navigation and color contrast requirements. This testing approach expands your user base while meeting legal compliance requirements.
API functionality testing validates the backbone of modern applications. You need to verify that your APIs handle requests correctly, return appropriate responses and maintain data integrity across different scenarios. This testing covers:
- Authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Data validation and error handling
- Response time and payload accuracy
- Integration compatibility with third-party services
API testing tools like Postman, REST Assured and SoapUI streamline the validation process. These platforms allow you to create automated test suites that verify endpoint functionality, data formats and security protocols.
Security and performance testing require dedicated environments that mirror production conditions. You should implement continuous monitoring to track security vulnerabilities and performance degradation over time. Regular security audits combined with performance benchmarking create a robust quality assurance framework that protects both your application and its users.
➢ Maintaining Clear Documentation and Defect Tracking Systems
Effective documentation is crucial for successful quality assurance processes. To maintain visibility throughout your testing lifecycle, you need comprehensive bug tracking tools like Jira or Bugzilla. These platforms allow for seamless integration between test case management and defect reporting, creating a unified system for quality tracking.
Best Practices for Defect Reporting
When it comes to defect reporting, there are certain best practices you should follow:
- Provide clear and reproducible steps that any team member can understand and follow.
- Include specific details about the environment in which the issue occurred, such as browser or device specifications.
- Clearly outline the expected behavior versus the actual behavior in your reproduction instructions.
- Whenever possible, include visual evidence of the issue through screenshots or video recordings.
- Classify each defect based on its severity and priority, taking into account its impact on the business.
The Importance of Integration
It’s essential to integrate your defect tracking system with specialized testing areas. This ensures that every finding from activities such as security testing, penetration testing, or performance/load testing using tools like LoadRunner or Apache JMeter is properly documented. The same level of meticulous recording should also apply to results from accessibility testing following WCAG guidelines and outcomes from API functionality testing.
Establishing Traceability Links
To ensure complete coverage and enable quick impact analysis when issues arise during your quality assurance processes, you should establish traceability links connecting requirements, test cases and defects. This approach allows you to easily track the relationship between these elements and understand how changes or problems in one area may affect others.
➢ Embracing Agile and DevOps Methodologies in QA Processes
Agile QA practices transform traditional testing approaches by embedding quality assurance directly into iterative development cycles. You can implement short testing sprints that align with development iterations, enabling rapid feedback loops and continuous validation of features. This methodology encourages collaborative planning sessions where testers participate in story estimation and acceptance criteria definition from the project’s inception.
Incorporating manual testing strategies into your Agile approach can provide valuable insights that automated tests might miss. These strategies allow for a more nuanced understanding of user experience and software functionality.
DevOps integration with QA creates seamless pipelines where testing becomes an automated, continuous process. You should establish automated test suites that trigger during code commits, incorporating security testing and penetration testing into your deployment pipeline. Tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI can orchestrate these processes, ensuring every code change undergoes comprehensive validation.
Your testing strategy should include:
- Performance/load testing tools like LoadRunner and Apache JMeter integrated into CI/CD pipelines
- Accessibility testing following WCAG guidelines automated through tools like axe-core
- API functionality testing executed before UI deployment using Postman or REST Assured
This integrated approach reduces manual intervention while maintaining rigorous quality standards. You gain faster release cycles without compromising software reliability, as automated checks catch issues before they reach production environments.
➢ Commitment to Continuous Learning and Adaptation in QA
The software testing world is always changing, so QA professionals must keep up with new technologies and methods. AI-driven testing techniques are changing the way we create test cases, predict defects and optimize test execution. These smart systems can look at patterns in your code and point out high-risk areas that need extra testing.
You need to continuously update your expertise across diverse testing domains:
- Security testing and penetration testing methodologies to address evolving cyber threats
- Performance/load testing tools like LoadRunner and Apache JMeter for handling increased system demands
- Accessibility testing compliance with WCAG guidelines ensuring inclusive user experiences
- API functionality testing techniques as microservices architectures become standard
New industry standards often change how QA works. Automation frameworks come up regularly, promising better efficiency and reliability. To stay competitive, you should engage with QA communities, go to conferences, and get certified.
Successful QA teams create an environment where learning is a priority and sharing knowledge is common practice. By holding regular training sessions, evaluating tools and trying out new testing methods, you can keep your skills sharp and stay updated on industry changes